STUDY CASE 3 : CHAPTER 7 : ELECTRICAL SAFETY
MOHAMAD BADRUDDIN BIN AZRI
02DEE17F2021
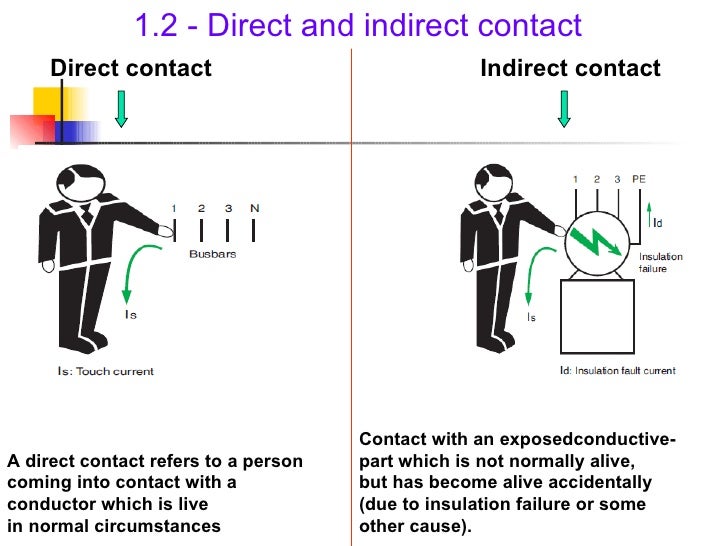
INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL HAZARD
Electricity is safe to use but may become dangerous in careless hands.It may cause fire,damage and fatal or non-fatal accidents to personal, unless appropriate elementary precautions are taken.This danger from electricity can be avoided by using good quality equipment,material,proper wiring and installation as well as efficient maintenance and upkeep or protective device.
In large factories of power system or other electrical installations,it is not always feasible for the engineers and supervisors to explain at length and as often as necessary,all aspects off safety precautions to every new staff member not to train him against all possible hazard within a short period.
IMPROPER GROUNDING HAZARDS
- Tools plugged into improperly grounded circuits may become energized
- Some of the most frequently violated OSHA standards
- Broken wire or plug on entension cord
- Unwanted voltage will not be safely eliminated
- Leakage of current to the ground
- Removal of the ground pin
- Removing of the ground pin removes a vital safety feature

When an electrical system is not grounded properly, a hazard exists. The most common OSHA electrical violation is improper grounding of equipment and circuitry. The metal parts of an electrical wiring system that we touch (switch plates, ceiling light fixtures, conduit, etc.) should be grounded and at 0 volts. If the system is not grounded properly, these parts may become energized. Metal parts of motors, appliances, or electronics that are plugged into improperly grounded circuits may be energized. When a circuit is not grounded properly, a hazard exists because unwanted voltage cannot be safely eliminated. If there is no safe path to ground for fault currents, exposed metal parts in damaged appliances can become energized.
OVERLOAD HAZARD
OVERLOAD HAZARD
- Too many devices plugged into a circuit,causing heated wires and possibly a fire
- Damaged tools overheating
- Lack of overcurrent protection
- Wire insulation melting,which may cause arcing and a fire in the area where the overload exists,even inside a wall


If too many devices are plugged into a circuit, the electrical current will heat the wires to a very high temperature. If any one tool uses too much current, the wires will heat up.The temperature of the wires can be high enough to cause a fire. If their insulation melts, arcing may occur. Arcing can cause a fire in the area where the overload exists, even inside a wall.
WET CONDITIONS
- Wet conditions are hazardous
- Damaged insulation will increase the hazard in wet location
- Using tools in wet locations
- Water increase the risk of electric shock
- Damp, wet and humid conditions are very hazardous while working with electricity
- Damaged insulation increase the hazard


WHAT WILL HAPPEN IF NOT CONTROL
Damaged insulation, equipment, or tools can expose you to live electrical parts. A damaged tool may not be grounded properly, so the housing of the tool may be energized, causing you to receive a shock. Improperly grounded metal switch plates and ceiling lights are especially hazardous in wet conditions. If you touch a live electrical component with an uninsulated hand tool, you are more likely to receive a shock when standing in water.
PREVENTIVE MEASURE IN ELECTRICAL SAFETY
CREATE A SAFE WORKING ENVIRONMENT
LOCKOUT AND TAGGING OUT CIRCUITS AND EQUIPMENT
- Apply locks to power source after de-energizing
- Tag deactivated controls
- Tag de-energized equipment and circuits at all points where they can be energized
- Tags must identify equipment or circuits being worked on
WHAT WILL HAPPEN IF NOT CONTROL
Lockout-tagout (LOTO) or lock and tag is a safety procedure which is used in industry and research settings to ensure that dangerous machines are properly shut off and not able to be started up again prior to the completion of maintenance or servicing work. It requires that hazardous energy sources be "isolated and rendered inoperative" before work is started on the equipment in question. The isolated power sources are then locked and a tag is placed on the lock identifying the worker who has placed it. The worker then holds the key for the lock ensuring that only he or she can remove the lock and start the machine. This prevents accidental startup of a machine while it is in a hazardous state or while a worker is in direct contact with it.
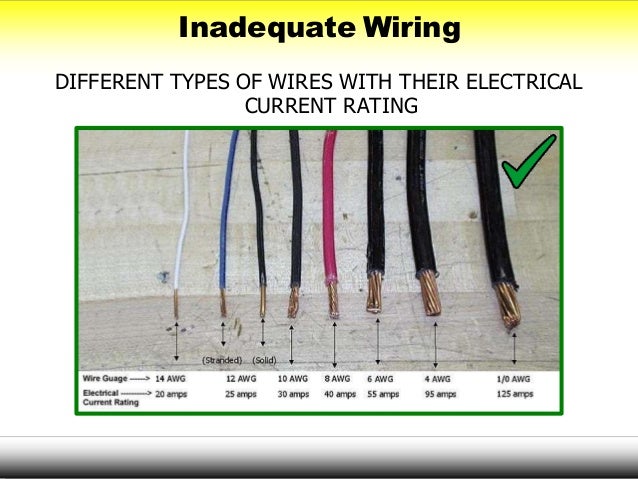
OVERLOAD WIRING BY USING THE RIGHT SIZE AND TYPE OF WIRE
- If too many devices are connected into a circuit,the current will heat the wires to a very high temperature, which may cause a fire
- If the fire insulation melts,arcing may occur and cause a fire in the exists, even inside a wall

TYPE OF WIRE
WIRE COLOUR CODE

WHAT WILL HAPPEN IF NOT CONTROL
Choose the right size wire for the amount of current
expected in a circuit. The wire must be able to handle the current safely. The wire’s insulation must be appropriate for the voltage and tough enough for the environment. Connections need to be reliable and protected.
CONCLUSION
Protective relays are used to detect electrical faults and to alarm, disconnects or shutdown the faulted apparatus to provide personnel safety and equipment protections. Then, a protective relay does not prevent the appearance of fault rather takes action only after a fault has occured in the system.

Comments
Post a Comment